Varicose veins (varicose veins) are a disease accompanied by an increase in length, the formation of pathological serpentine tortuosity of the veins, irreversible saccular enlargements of their lumen and valvular insufficiency. The organs of the lower pelvis are involved in the varicose process. The mechanisms of development of the disease are different. Doctors include the perineal region, external genitalia and internal genitalia as atypical locations.
General pathology information
The process of blood circulation in the veins takes place in such a way that under physiological conditions prerequisites are created for the development of stagnation and outflow of blood.
Varicose veins of the vulva (VV) - vasodilation of the external genitalia. The disease manifests itself in women who suffer from varicose veins of the pelvis and legs, as well as in pregnant women. In 30% of cases, pelvic varicose veins affect the perineum and vulva.
The onset of treatment for the disease is delayed due to localization in an intimate place. Women are shy. In some cases, patients do not experience pain or discomfort. But varicose veins of the lips during pregnancy and not only when carrying a fetus lead to complications: clogging of the veins with a thrombus (thromboembolism), disorders of sexual sensitivity, pain in the perineum, psycho-emotional problems and family conflicts.
The mechanisms of the occurrence of congestion of the vessels of the pelvis are not fully disclosed. The cause of the primary form of the disease is called a dysfunction of the valves of the gonadal (ovarian) veins. This causes blood to flow back and increases the pressure in the venous lymph nodes in the lower pelvis. Valve insufficiency can be acquired or congenital. It gets worse with age or with pregnancy.
The secondary form of VVV of the pelvic organs is associated with gynecological pathologies: endometriosis, tumors of the pelvic organs.
Diagnosis of the disease is difficult due to the fact that there are no specific symptoms of its course. It is based on the results of ultrasound (ultrasound).
To distinguish between primary and secondary forms of pathology, the Valsalva test is used during ultrasound examination. With a secondary cause of pelvic varicose veins, it is negative.
Varicose veins of the lips with VBT
To make a diagnosis of varicose veins of the lips, a medical examination is required. Symptoms of the disease are as follows:
- varicose veins on the genitals;
- pain in the external genital area;
- a feeling of heaviness and burning in the perineum;
- swelling of the perineum at the end of the day.
Chronic pelvic pain is less common (in 30% of cases).
After the diagnosis is established, a study is carried out in order to identify the degree of complexity of the pathological process and to prescribe adequate treatment. Several events are organized:
- examination of the veins of the perineum and legs by ultrasound CT angiography - USAS;
- perform ultrasound of pelvic vessels, including vaginal, uterine, parametric, ovarian, iliac, inferior vena cava, and renal veins;
- as indicated, multispiral computed tomography (MSCT), selective ovarycography and pelvic venography (SOFT) are performed.
Doctors call a characteristic property of varicose veins on the lips with VBT that the disease progresses steadily and is associated with the transformation of the intrapelvic veins.
Treatment of varicose veins of the vulva with varicose veins of the lower pelvis
IV treatment is prescribed based on symptoms and diagnostic results.
In complex drug therapy for the treatment of chronic systemic venous pathology, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and phlebotropic drugs are prescribed.
Prescribe pharmacotherapy with antiplatelet agents, intrapelvic blockade with antihypoxants, physiotherapy with ultrasound, therapeutic exercises. Antioxidants and enterobiotics are added to the therapy.
According to the indications, phlebosclerosing treatment is carried out - sclerotherapy. The vessel is "sealed" with drugs and a laser. It stops working. The procedure does not use special methods of anesthesia. It is performed on an outpatient basis and produces a cosmetic effect.
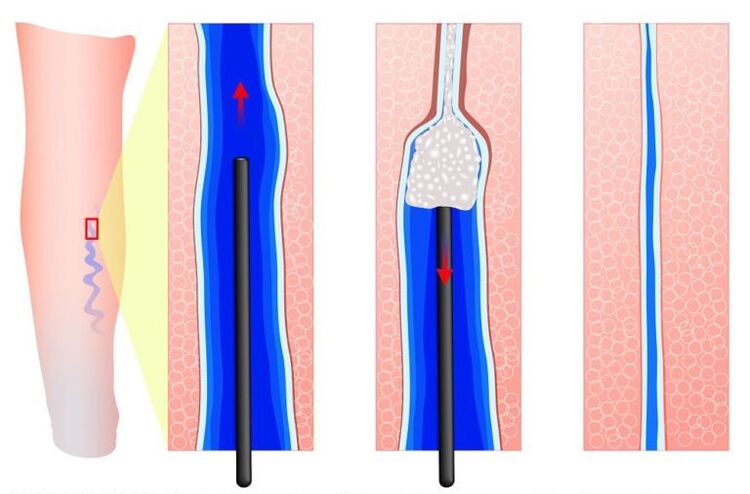
If there is a plethora of pelvic veins, expansion and backflow of blood into the gonadal (ovarian) veins, surgery to remove the veins is indicated. In case of varicose enlargement of the labia minora, it is removed.
Varicose veins of the vulva during pregnancy
Pregnancy is the most common first risk factor leading to the onset of VVV. A significant and sustained increase in the concentration of progesterone from the early stages of pregnancy reduces venous tone and worsens impaired blood circulation. Additionally, VBT, involving the perineum and vulva, is associated with compression of the large veins in the retroperitoneal region (iliac veins and inferior vena cava) by the pregnant uterus.

Doctors recommend compression garments during pregnancy.
Varicose veins of the vulva are often bilateral. Signs of illness:
- a pronounced increase in the veins of the vulva at a period of 18-24 weeks with the first pregnancy, starting at 12 weeks with a repeated pregnancy;
- discomfort in the groin;
- pulling, aching, dull pain in the pelvic area;
- pain during intercourse;
- itching of the vulva;
- swelling of the genitals and perineum.
Signs of pathology progress during pregnancy. In addition to increasing the size of varicose veins, its compaction is determined by the third trimester. A characteristic symptom of IV is its combination with inguinal varicose veins during pregnancy or varicose veins in the legs.
Instrumental examination of varicose veins of the lips in pregnant women is limited to their ultrasound, as well as ultrasound of the legs, since painful changes in the venous bed undergo involution in the postpartum period.
In most cases (about 80%), from the first days of childbirth, the symptoms of varicose veins during pregnancy begin to decrease and are minimized 2 to 8 months after the baby is born. A complete return of the diameter of the vessels to their original values does not occur.
In 4-8% of women, the IV does not go away after childbirth and the disease progresses.
An interesting feature is the relationship between the end of the breastfeeding period or a reduction in breastfeeding volume on the rate of disappearance of groin varicose veins in women. A shortened lactation period is accompanied by a decrease and disappearance of dilated veins and vice versa. This proves that varicose veins of the perineum during pregnancy are associated with changes in hormonal levels.
Treatment of varicose veins of the perineum during pregnancy
The basis of treatment for varicose veins during pregnancy is phlebotropic treatment. In most fertile women, IV begins in trimesters II and III. During this period, preparations of diosmin can be used. The severity of the symptoms of the pathology is reduced by the purified micronized flavonoid fraction. The itching is relieved by zinc paste and histamine H1 receptor blockers.
Prophylactic low molecular weight heparin prevents venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism (blockage of blood vessels).
As an option for the treatment of compression, it is prescribed to wear tight elastic underwear with the help of latex or gauze pillows. It relieves puffiness of the lips and the feeling of heaviness. The special compression jersey for women with vulvar varicose veins helps a lot.
If a complication develops, such as local thrombophlebitis, surgical treatment is necessary.
When a conglomerate of varicose veins is found on the genitals, the question arises of the method of delivery. Natural childbirth is allowed with varicose veins of the vulva. On the contrary, the risks of surgery during a cesarean section are higher than the appearance of bleeding from painful vessels during childbirth. This rarely happens. But with varicose veins of the vagina, a cesarean section is often performed.
Prevention of varicose veins of the lips
The main factor in the formation of varicose veins in the groin is carrying the fetus. It is difficult to name preventive methods, taking into account that during pregnancy there are a number of restrictions on many therapeutic measures. Some tips to follow:
- exclude physical and static constraints;
- diet;
- perform therapeutic exercises, in which the movements accelerate the flow of blood from the legs and lower pelvic organs;
- in case of disturbance of the work of the veins, the presence of varicose veins before pregnancy, it is necessary to take phlebotropic drugs, wear compression underwear.
An effective method of prevention is considered to be an operation of the ovarian veins, surgery for other pathologies associated with varicose veins. This reduces the phenomenon of pelvic venous congestion, reduces the risk of varicose veins in the lips.
Vulvar varicose veins are a common disease in women with varicose veins of the pelvis, legs or during gestation.
In order to improve the quality of treatment of patients with chronic venous diseases, it is important to detect the disease, differentiate the methods of diagnosis and treatment of this disease.




































