From this article, you will learn: why varicose veins of small pelvis is considered to be a separate disease, and this form of varicose veins of the legs; in whom this disease can occur and why. Manifestations and diagnosis of this pathology, as it is properly treated, the chances of recovery.

Varicose veins of the pelvis – it is the weakening of the blood vessel walls of internal or external inflammation of the blood vessels in the pelvic area, which leads to excess enlargement of their diameter. Varicose changed veins are not able to ensure the outflow of blood from the pelvic organs, which leads to its stagnation, and the complete destruction of the vascular wall. As a result – violation of the structure and function of the female reproductive system.
The initial phase of the disease cause only mild discomfort in the area of the external genitalia and the lower abdomen. Women with advanced forms of pelvic varicose veins obsessed with from constant severe pain, various gynecological diseases, infertile, have a cosmetic defect in the form of a convoluted widespread inflammation of the glands in the perineum, the genital lips, or at the entrance to the vagina.
The disease can be completely cured, but to prevent relapse, it is required a lifetime of prevention. Deal with this problem together vascular surgeons, obstetrician-gynecologists.
Varicose veins of small pelvis in men in this form, as in women not the case. But such a disease exists – varicocele. The mechanisms of the emergence and manifestations are similar to those in pelvic varicose veins. Enlargement of the veins occurs in the egg and on the move seed of the cable due to the fact that in the left vienna testicular stagnant blood. She is back threw from the left renal vein, which empties in vienna.
The essence of the pathology, how serious it is
External and internal female sexual organs well krovosnabjaemah. In order to ensure sufficient outflow of blood we need a powerful network of inflammation of the blood vessels. So the venous system of the pelvis in women is well developed. Each vienna has a strong wall, which is equipped with valves, associated with a number of around the veins. It all forms together seamlessly functional venous network of the pelvic region which collects blood from the groin, external genital organs (the vagina, the vaginal entrance), special structures (ovaries, uterus), and transports it in the lower Polow vienna.
Varicose changed veins of the pelvis varies from the healthy to the fact that:
- Are expanded in diameter;
- Overflowing with blood;
- Unnecessarily convoluted;
- They have a protrusion in the form of nodes;
- Flabby and weak.
Pelvic veins, is affected by varicose veins, can collect the blood from the external genital and other organs, but they are not able to correctly transfer it into a larger container (vena cava). This leads to the fact, that the blood stagnating in the pan, and penetrates through the vein wall, affects the substance of which should not. They become swollen, inflamed and lose their function.
But most of all, varicose veins pelvic dangerous:
- Various disorders of the ovaries;
- Uterine bleeding and a variety of disorders;
- Infertility, the threat of interruption of pregnancy and the impossibility of a natural birth;
- The formation of blood clots in the lumen of the varicose changed veins, threatening their lead from a place of education and migration on the heart and blood vessels of the lungs. It is the most dangerous complication, life – threatening thromboembolism of the pulmonary artery (PE).
Reasons
Basically varicose veins of the pelvis occurs in sexually mature women:
- To 20 years – 20%;
- 20-30 years – 30%
- 30 – 45 years – 50%
Mechanisms of varicose reincarnation of the venous system of the pelvis:
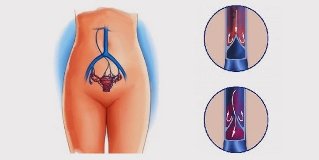
- (in 80%). They are the biggest trunk of the vein, which collect blood from the uterus and ovaries and carry her directly into the cavity (right) or in the kidney (left) veins. If failure occurs, it is completely blocking the venous outflow.
- Uniform weakening or destruction of the vein wall all the pelvic veins are all at the same time extend and are not able to shrink, to push the blood in the overlapping department.
- Reverse casting of blood from the deep veins of the thigh in the surface of a sexual vein, which collects blood from the groin and the external genital organs, prevents the outflow. As a result, the pressure in it rises, and its trunk and all tributaries of the varicose extend.
The immediate reasons for the launching of these mechanisms may be so:
- Congenital weakness or dysplasia (underdevelopment) of the venous wall and valves.
- Hormonal realignment in a woman's body (puberty, pregnancy, menopause, diseases of the ovaries).
- Frequent inflammatory processes, endometriosis, surgery, adhesive process in the pelvis.
- Moved thrombosis and thrombophlebitis of the pelvic veins.
- Heavy physical labor.
- A longer stay in position lying down or sitting.
- Overweight.
- Pregnancy and childbirth.
- Regular interruption of sexual intercourse over the years, especially in the absence of orgasm.
- Bend uterus posteriorly or front.
- Tumors of the small pelvis.
- Ptosis of the uterus.
Extent varicose veins – classification
On anatomical sex (the appearance of) varicose veins of small pelvis is divided into three kinds:
- Venous plethora in the pan;
- Perineal varicose veins, etc.;
- The combined form.
For the reflection of the character of the pathological changes of the disease is divided into three stages:
- The first – dilated blood vessels of any of the organ plexus of the pelvis do not exceed in diameter of 0.5 cm, unnecessarily convoluted.
- The second – the diameter of the veins increases up to 1 cm, the process is extended not only to plexus organs(vaginal, ovaries), but also around them (okolomatocnah fiber).
- The third expansion (ectasia) of more than 1 cm, affects all the blood vessels – intraorganic, about bodies, and luggage space (the trunk of the ovarian axis vienna).
The higher is the degree of the disease, the worse the dilated veins and harder to stagnation of blood in the pelvis.
The characteristic symptoms of
Women with varicose veins of the pelvis note:
- Persistent or recurrent abdominal pain, increasing at night or after exertion predominantly in the second half of the cycle (closer to the moon). In the 3 degrees of pain can be very debilitating.
- Itching, burning, swelling and cyanosis of the genital organs.
- Painful menstruation and sexual intercourse.
- Abundant menstruation and uterine bleeding, irregular cycle.
- The inability to get pregnant.
- The thickened knotty veins in the area of the perineum and the labia.
- Frequent painful urination.
- Clearly expressed manifestations of premenstrual syndrome.

Diagnosis
For confirmation of the diagnosis are carried out:
- ULTRASOUND through the abdomen and through the vagina (transvaginal) by using special sensors – Doppler, and two-sided treatment of the veins of the pelvis. The easiest and most informative method.
- Endovascular phlebography – the introduction of specific drugs in ovarian vienna.
- Computed tomography with enhancement.
- A diagnostic laparoscopy.
Methods of treatment
Varicose veins of small pelvis together treats vascular surgeons or obstetrician-gynecologists. According to modern ideas, the treatment consists of the following areas:
- Normalization of lifestyle;
- Conservative treatment the treatment;
- Compression and other therapies;
- Surgical treatment.
To treat varicose veins of the pelvis is possible. For this the experts form the individual treatment plan, and sick women must adhere to for life therapeutic and preventive recommendations.
1. Normalization of lifestyle
Because of the bad way of life serves as a prerequisite and the immediate cause of the formation of varicose pelvic veins, its normalization will help get:
- Exclude a longer stay in a sitting position or standing up (more than 2-3 hours without a break).
- Avoid lifting weights and give up hard physical work.
- During the day, start unloading exercises for the pelvic floor (exercises birch, round) or just lie 10-15 minutes with rose above the level of the body pans.
- Weight reduction (in the case of obesity).
- Do not take a hot bath, replace it with douches.
- Renounce alcohol and smoking.
2. Medical therapy
Treatment of varicose pelvic veins of any degree is not possible without medical support. In the first instance is a major medical event, while the second and third complements the comprehensive treatment.
These drugs are used:
- Special preparations – they strengthen the venous vessels.
- Anticoagulant – thins the blood, facilitate its promotion on the containers.
- Drugs, improve microcirculation.
Another group of drugs are prescribed with regard to existing derogations in the body:
- Drugs of female sex hormones (at dishormonal infringements).
- Painkillers and anti-inflammatory agents.
- Preparations for stopping the blood – styptic medication to treat uterine bleeding.
3. Compression therapy
One of the effective remedies in the treatment of varicose veins in the area of the external genitalia and the perineum is a compression effects. The principle of this method is similar to the use of elastic bandages during the varicose veins on the legs. Compression (compression) surface of the vein from the outside contributes to their emptying blood. To create such an effect are able to special tights or shorts of compression treatment of the knitted fabric. You can buy them in specialized pharmacies, stores, showrooms, health care, individually pull out to the desired size and strength of compression.
Sclerotherapy – a puncture of the varicose dilated veins with the introduction of the height of special drugs that cause her to cobble together. Such treatment is carried out at the outer (subcutaneous) pelvic varicose veins without hospitalization in the hospital. The internal veins can also be treated, but this procedure is technically more complex and takes place in the operating environment.
4. Surgical treatment
Varicose veins of small pelvis it is better to treat functional by:
- 2-3 degrees of the disease;
- Fast progression of the disease;
- Planning a pregnancy;
- The expression of the pain syndrome;
- Regular uterine bleeding and other gynecological disorders.
The basic types of operations on the pelvic varicose veins:
- Laparoscopic – special operations through punctures on the abdomen. Perform the ligation, the excess or the removal of the ovarian axis vienna. In this way it is eliminated the reverse casting of blood on her.
- The removal of the varicose dilated veins – through small punctures or incisions of the skin are altered subcutaneous veins, tied outdoor sex vienna at the confluence of the femoral vessels.
- Gynecological surgeries – the removal of the tumor, removal of bends of the uterus.
Weather
If left untreated varicose dilated veins of the pelvis, time is even more spread out (in 95%), which faces dangerous complications. For the remaining 5% of women with subcutaneous varicose veins crotch 1-2 degrees, which appeared after the birth, the pathology is not stronger, but will never pass by itself.
If left untreated the disease, it is possible to achieve complete recovery (10-50% depending on the degree), or significant improvement of the conditions (45-50%), especially in the case of a combination of surgical techniques with a conservative. But in any case, after a comprehensive treatment should be held a lifetime of prevention, which consists in the adherence to recommendations on lifestyle, regular health or compression support to the weakened veins.




































