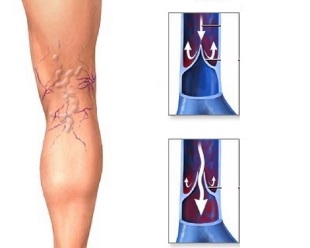
Varicose veins (varices) is one of the most common and oldest diseases of the cardiovascular system, which opened even from the days of ancient Egypt. With the help of the egyptian papyri and the excavations was found a mummy with signs of varicose veins. This disease has taken and the famous ancient physicians: Oath, Galen, Avicenna, and later Troyanova, Trendelenburg. And so then, this disease has not lost its relevance in modern medicine. Definition of "varicose veins" comes from the Latin word "varix", which means "expansion", so the disease got the name "Varicose veins". This disease is characterized by enlargement and an increase in the length of the peripheral veins in the form of a serpentine tortuosity (deformation), as well as a violation of the outflow of blood from it arising due to the failure of the valve apparatus and the weakening of their walls. The disease most often affects the veins of the lower extremities, because the main burden of the outflow of the blood (large volume) falls on them, therefore, prefers to just this part. Varicose veins occurs in about 17 - 25% of the population. At a young age the disease occurs as well as in boys, in girls. In the mature of the same age women sick 2 - 3 times more often than men, due to hormonal adjustments of the female body (menstruation, pregnancy, menopause).
Causes and risk factors in the development of varicose veins
The exact cause of the disease is unknown, all we know is that under the influence of some factors is developing the release valve, the pressure increase and loss of elasticity of the vascular wall of superficial and connecting veins. Risk factors:
- Genetic predisposition: the transfer of varicose veins by inheritance occurs due to mutation of the gene responsible for the structure of the walls of the container, as a result of his mutation, children are born with a congenital weakness of the connective or muscular tissue of the wall of the vessel, and either the disadvantage of its valves (the lack of their number) and, in consequence, there is the weakness of walls of blood vessels and increased pressure in the veins.
- Hormonal changes (pregnancy, menopause): during pregnancy changes the hormonal composition of the body (increased levels of estrogen and reduced estrogen levels), which affect the formation of blood clotting factors (sudafed), lowering the tone of the venous walls (due to the destruction of collagen and elastic fibers of the vessel wall), all this leads to the formation of blood clots, blockage of blood vessels and their deformation.
- Obesity : being overweight leads to a sedentary lifestyle, due to which there is slowing of blood circulation, plus excess body fat increases the intra-abdominal pressure, which impairs the flow of blood in the veins, which develops, stagnates in the veins and the possible development of the disease.
- Diabetes mellitus :chronic elevated blood sugar over time damages the walls of blood vessels, which is a favorable environment for the development of blood clots.
- Alcohol abuse : excessive use of alcohol leads to dehydration and thickening of the blood, in consequence, they form blood clots that clog veins and violation of the outflow of blood.
- Lifting weights (movers),long walk the next years, or worth the work (sellers, conductors): is associated with a decrease in muscle tone, increased intra-abdominal pressure, and due to the slowdown and disorders of the blood flow to the heart and the development of its stagnation in the lower extremities.
- Congenital blood clotting disorders: congenital hypercoagulation (excessive production of factors of the folding of the blood) leads to the formation of blood clots and disruption of the support of the circulation in the vessels.
- Inappropriate food: a lack of certain vitamins in food (vit.C, E, P, vegetable fibers play a role in strengthening the walls of blood vessels and improve blood circulation).
- Wearing tight underwear: permanent wear that leads to mechanical compression of the vein, causing disorders of the venous outflow from the lower extremities.
- Chronic constipation : frequent increase of the intra-abdominal pressure (during exertion) leads to the difficulty of outflow of blood from the lower extremities.
- Frequent walking on high heels: the lack of movement of the muscles of the lower extremities and the development of stagnation.
- The hottest time of the year: frequent thirst leading to dehydration occurs thickening of the blood and formation of blood clots.
- Related diseases of the cardiovascular system, or kidney disease: is disturbed by the outflow of venous blood (insufficiency of the heart valves, congenital defects).
- An overdose of drugs increasing blood clotting of blood: the risk of developing blood clots and blockage of blood vessels.
- Surgical intervention:the loss of a certain amount of blood, is not a comfortable position on the operating table (the compression of certain blood vessels), which leads to the risk of blood clots.
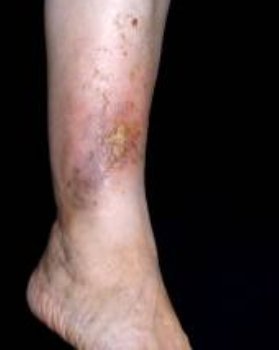
Complications of varicose veins
- The formation of blood clots due to stagnation of blood in the veins;
- lead a clot and blockage of blood vessels which coincides with its diameter;
- thrombophlebitis (due to the education of the clot in the lumen of vienna's happening to her inflammation of the vascular wall);
- thromboembolism of the pulmonary artery (detached thrombus formation on the flow of blood gets into chylopericardium artery, which is involved in the circulation on a small scale. If the diameter of the precipitate coincides with the diameter of the trunk of this artery, then it can result in sudden death. If it is a clot less in diameter, then it runs away into the branches of the pulmonary arteries and trigger a heart attack the lungs or pulmonary edema).
- trophic ulcers or eczema on the feet due to eating disorders (broken blood circulation leads to lack of oxygen to the tissues, which is the most important meal of the tissues);
- swelling of various parts of the body due to stagnation in the veins (they are soft, flexible, cyanotic color, their formation is not dependent on time of day, most often they are formed in the affected area);
- dermatitis (inflammation of the skin in the affected area) due to failure of the power supply to this property;
- change the color of the skin in the area affected area;
- seal the subcutaneous fat of fiber in the area of the affected area through the swelling.
The diagnosis of varicose veins
- The flagellum (functional) pattern (definition of the continuity of the veins and their valves): Troyanova - Trendelenburg,Pratt, Shania, Delbe-Pertusa, and more. One of the most common test Troyanova - Trendelenburg in the care that the patient stay in a horizontal position, raise leg at 45 0, the doctor makes a stroking from the feet up (thus emptied superficial vein), then straps on the upper part of the thigh and asks the patient to stand up, in the standard filling of the veins of the lower extremities should occur more than 15 seconds;
- Duplex ultrasound examination of the veins (ultrasound angioscanning) is the most informative method, allows the assessment of blood flow in the vessel, and see for yourself the container;
- Dopplerhophy - method, which is only assessed blood flow in this vessel;
- Phlebography - the introduction of a contrast substance intravenously, and the study of x-ray images;
- Phleboscintigraphy - intravenous administration of radiopharmaceuticals and observations on the special equipment.
Treatment of varicose veins
Nonsurgical treatment

- Folk methods of treatment (as an adjunct to medical treatment): the wearing of compression knitted fabrics (stockings); special exercises (swimming, bike, skis, feet above your head about 20 0 towards the bed, special gymnastics ("bike" - lying on your back and evenly breathe in, imagine that you spin the wheel the pedal; alternately bend and straighten your legs in the ankle joint forward and backward) are used for the improvement of outflow of blood, but only in the not hard cases); jets (under a stream of water to the feet, gradually reduce the water temperature reaches the cold); sock trays (not hot) from a decoction of the bark of oak, chestnut, chamomile, st. john's wort; rubbing alcohol tincture of white flowers of acacia, the leaves of kalanchoe, apple cider vinegar; in thrombophlebitis treatment with leeches.
- The mode of the day: early morning slow walk from the bed (about 5-10 minutes), during sleep puts a pillow under your heel to lift your legs about at 15-20 0 to bed, the walk shall be relaxed, you cannot sit crossed leg on the leg, bandage the legs elastic bandage from the feet to the top of the thigh, the wearing of medical stockings, rational nutrition, to avoid any of boring movements and of any substances or factors that contribute to thickening of the blood, the exclusion of smoking, the prevention of constipation.
- Diet : the body of needed foods containing vitamins strengthen the walls of blood vessels and improve blood circulation: vitamin C (it contains with the citruses, tomatoes, rose hips, etc.), vitamin E (legumes, liver, egg yolk, green onions), vitamin P (grapefruit, walnut, black currant), bioflavonoids (dark cherries, sour cherries), copper (seafood). Sufficient daily amount of fluid at least 1.5 liters. Will be limited, and in the consumption of alcoholic beverages, coffee, marinades, smoked.
Surgical treatment
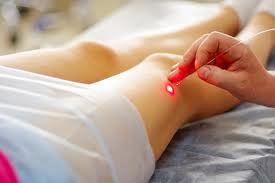
Phlebectomy:Indications for the removal of veins: extensive varicose veins, subcutaneous veins pathologically expanded, trophic violations of skin, which is not amenable to conservative treatment, acute thrombophlebitis, varicose subcutaneous veins is accompanied by a violation of the general condition (significant fatigue, swelling of the legs) of the patient. Contraindications to the removal of veins: coronary artery disease, severe infectious processes, the higher the age of the patient, pregnancy in 2 and 3 trimester, inflammatory processes on the legs (erysipelas inflammation, pyoderma, eczema). The advantages of surgical treatment: the only method of treatment in more advanced cases, the only radical way of correction valves of the deep veins. Disadvantages of surgical treatment: traumatic (cosmetic defect), requires anesthesia, it is necessary to set several days in the hospital under the supervision of a physician. Laser (endovascular microtermocoagulation) :Indications: the Combination of varicose veins with the following diseases: diseases of the cardiovascular system (coronary heart disease, high blood pressure), peripheral vascular disease (phlebitis, thrombophlebitis), with diseases of the respiratory tract (bronchial asthma, bronchitis, pleurisy), with diseases of the digestive system (cholecystitis, gastric ulcer and duodenal ulcer), diseases of the nervous system (craniocerebral traumas, neuroinfections), with diseases of the genitourinary system (pyelonephritis, endometritis, salpingitis), with diseases of the skin (dermatitis, Neurodermatitis), peritonitis, ulcers. Contraindications: people suffering from oncological diseases, diseases of the liver, kidney and heart in the stage of decompensation, cerebral sclerosis, pregnancy. Advantages: allows you to get rid of unpleasant vascular drawings, a quick procedure (15-20 minutes), does not require hospitalization, is a safe and painless, not traumatic to the vessel tissue and the surrounding tissue. Cons: not available everywhere method, honey method, in the removal of larger blood vessels is the possible thermal damage to the tissue, the possible emergence of scars and depigmentation (lightening) of the skin in the places of impact. Radiofrequency coagulation (ablation) of varicose veins: Indications: varicose disease with lesions of the trunk large and small subcutaneous veins, trophic ulcers due to the varicose veins. Contraindications: acute thrombophlebitis of subcutaneous veins, the inability of active walking, pregnancy, psychological disorders. Advantages: no cosmetic defects, painless, does not require hospitalization, is not in breach of the performance. Cons: the only drawback is the price of the procedure. Sclerotherapy: Indications: minor varicose veins, large varicose veins when using the duplex dopplerography, varicose veins in the early stages (when the damage only superficial veins. Contraindications: pregnancy and lactation, allergy to sclerosus, deep vein thrombosis, purulent-inflammatory diseases of the feet. Advantages: lower cost, compared with running, the fastest period of recovery, does not require a stay in the hospital (you can immediately go home), the best cosmetic result. Cons:impossible to get into a deep vein sclerosus, decreases efficiency-stirring sclerosus with blood, ineffective in neglected cases.




































